
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, injection molding stands out as one of the most efficient and versatile techniques for producing plastic components.
We share information, tips and things we've learned from our years in the rapid prototyping and plastic mold manufacturing industry.
What is Injection Molding and How Does it Work: Definition & Working Process
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, injection molding stands out as one of the most efficient and versatile techniques for producing plastic components. From everyday household items to advanced automotive parts, this process is the backbone of countless products we rely on daily. But what exactly is injection molding, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of this manufacturing marvel, exploring its definition, working process, and the advantages it offers.
Understanding Injection Molding
At its core, injection molding is a manufacturing process used to create parts by injecting molten material into a mold. This method is predominantly used for plastics, although metals and glass can also be molded using similar techniques. The process begins with choosing the right material, typically in the form of small pellets or granules. These materials are selected based on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance.
The Working Process of Injection Molding
The injection molding process can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Material Preparation: The journey begins with the selection and preparation of the raw material. Plastic pellets are fed into a hopper, where they are heated and melted through a combination of temperature control and mechanical mixing.
2. Injection Phase: Once the plastic is in a molten state, it is injected into a precisely designed mold under high pressure. This step is crucial, as it ensures that the material fills every part of the mold cavity, capturing all the intricate details of the design.
3. Cooling Phase: After the molten plastic is injected, it must cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help regulate temperature, allowing the material to harden into its final shape. This step is vital for ensuring the structural integrity of the product.
4. Ejection Phase: Once the part has sufficiently cooled and solidified, it is ejected from the mold using ejector pins or plates. A quality inspection is often conducted at this stage to check for any defects or inconsistencies.
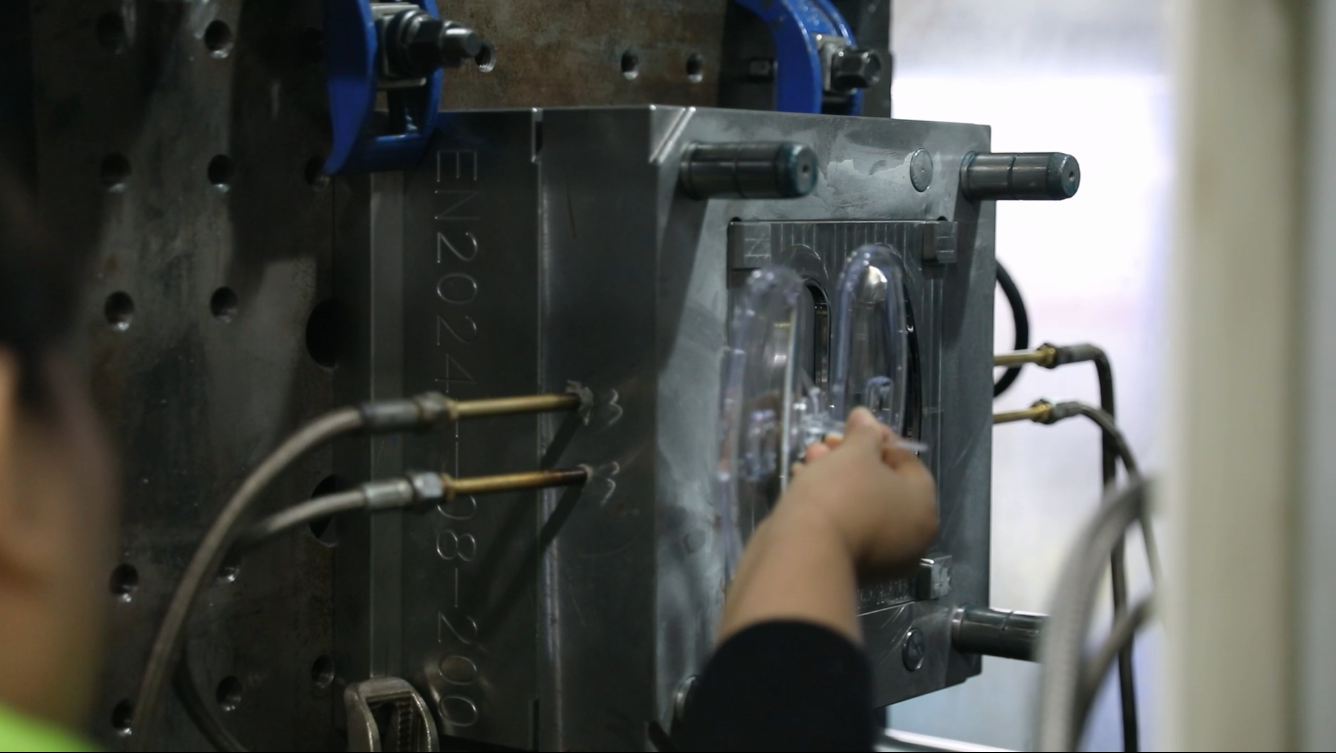
Key Components of an Injection Molding Machine
An injection molding machine consists of several critical components. The "hopper" is where the plastic pellets are stored before they enter the machine. The "screw and barrel" are responsible for melting and mixing the material, while the "mold" defines the final shape of the product. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Advantages of Injection Molding
One of the primary reasons injection molding is favored in manufacturing is its efficiency. The process allows for rapid production cycles, which is essential for mass production. Additionally, injection molding offers high precision and consistency, making it possible to create complex shapes that meet strict specifications.
Furthermore, this method minimizes waste, as excess material can often be recycled back into the process, making it an environmentally friendly option. The versatility of injection molding also allows manufacturers to experiment with a wide range of materials, including innovative bioplastics and sustainable options.
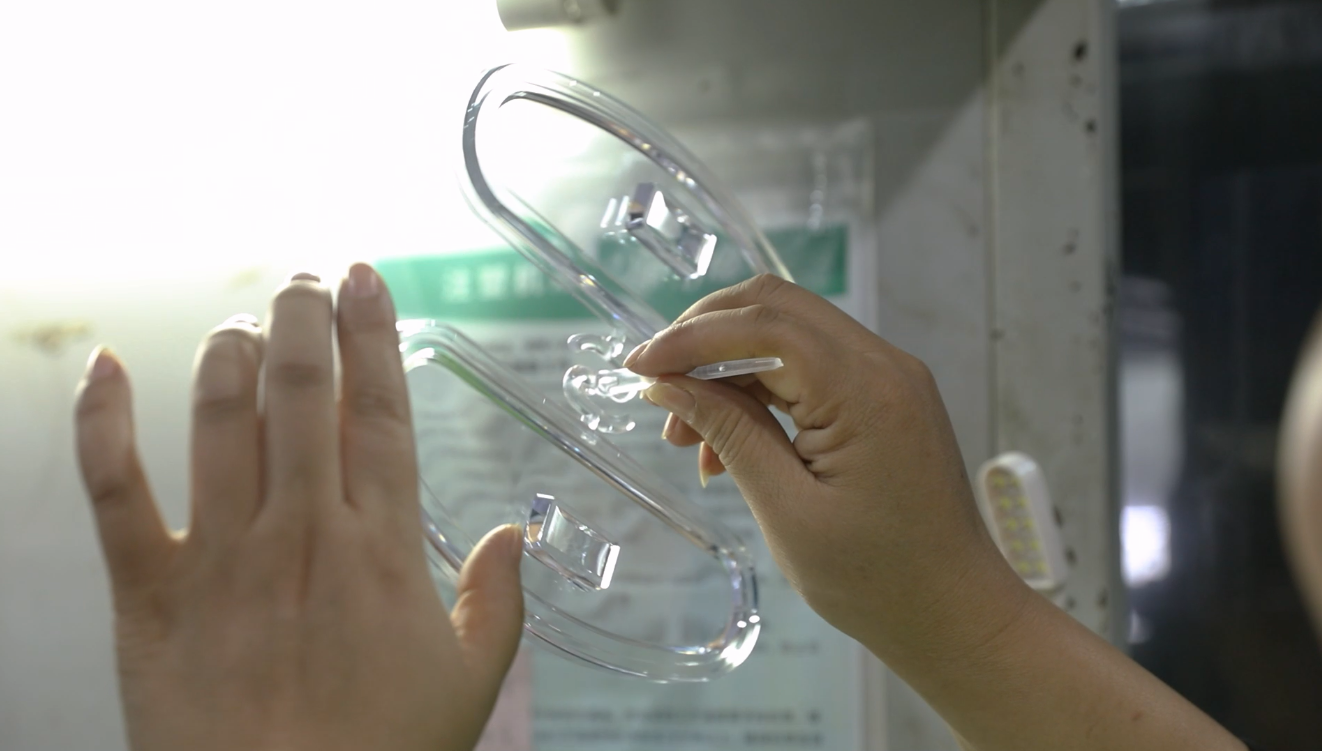

Applications of Injection Molding
The applications of injection molding are vast and varied. Industries such as automotive, consumer products, medical devices, and electronics all rely on this method to produce high-quality components. For instance, injection molding is used to create everything from intricate electronic housings to durable automotive parts, showcasing its adaptability and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Injection molding is more than just a manufacturing process; it is a crucial technology that shapes the products we use every day. Its ability to produce high-quality parts with speed and precision makes it an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. As innovations continue to emerge in materials and techniques, the future of injection molding looks bright, promising even greater possibilities for industries around the globe.
In a world where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, understanding the intricacies of injection molding is essential. Whether you’re a manufacturer looking to optimize your production or a consumer curious about how your favorite products are made, injection molding is a fascinating process that plays a vital role in our daily lives.