Design Considerations and Prototyping Importance of Design in the Mold Processing Design plays a pivotal role in the success of Injection Molding. A well-thought-out design not only ensures the funct
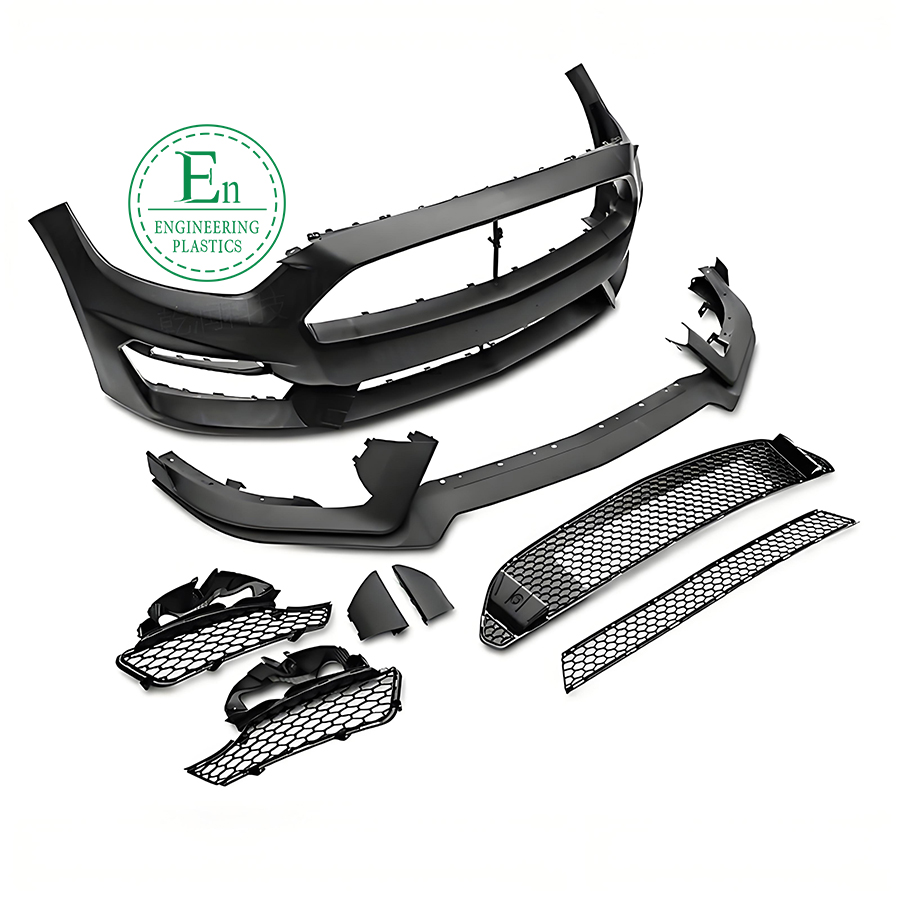
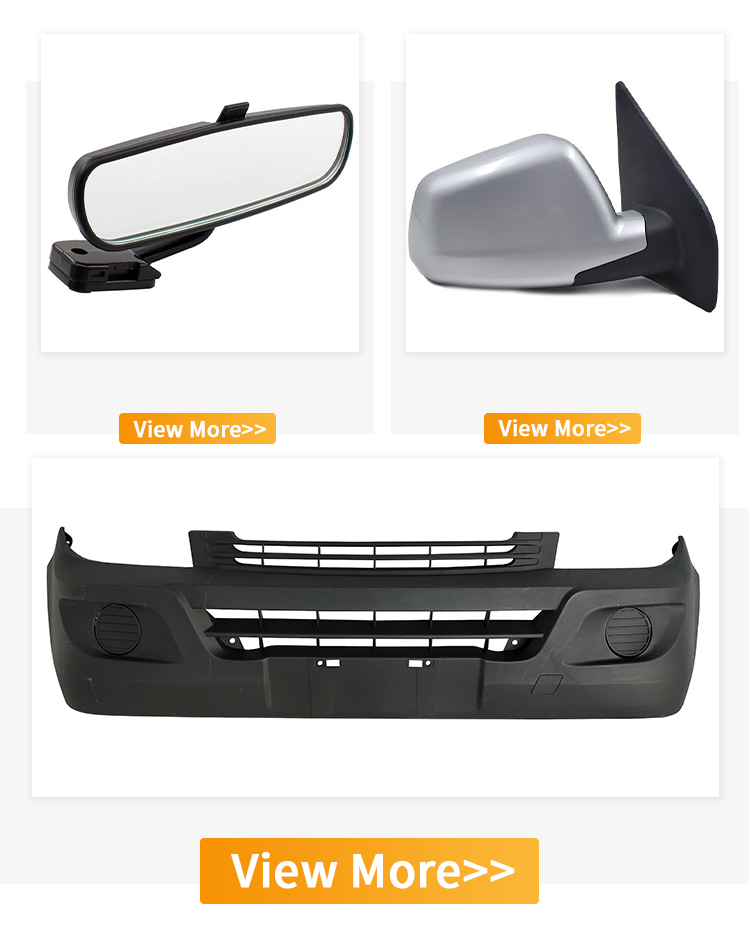
Automotive Moulding Injection








Design Considerations and Prototyping
Importance of Design in the Mold Processing
Design plays a pivotal role in the success of Injection Molding. A well-thought-out design not only ensures the functionality and aesthetics of the final product but also influences the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Proper design can minimize material usage, reduce cycle times, and prevent defects. It’s crucial to consider factors like wall thickness, rib design, and gate location during the design stage to optimize the molding process and the quality of the final product.
Designing Parts for Injection Molding
Uniform Wall Thickness: Aim for consistent wall thickness throughout the design to avoid issues like warping, sink marks, or incomplete filling.
Draft Angles: Incorporate draft angles to facilitate the easy release of the part from the mold.
Ribs and Gussets: Use ribs and gussets for added strength, but ensure they are not too thick to avoid shrinkage issues.
Gate Location: Carefully plan the gate location (where the molten plastic enters the mold) for efficient flow and minimal visual defects.
Avoid Sharp Corners: Round off corners to reduce stress concentrations and improve flow.
Consider Shrinkage: Account for the material’s shrinkage properties in the design to ensure dimensional accuracy.
Role of Prototyping and 3D Printing in Refining Designs
Prototyping is a critical step in refining designs for injection molding. It allows for the testing and validation of design concepts before investing in expensive mold tooling. 3D printing, in particular, has revolutionized prototyping.
With 3D printing, designers can quickly create prototypes that closely mimic the properties of injection-molded parts. This enables the identification and rectification of design flaws early in the development process. Prototyping also provides a tangible model for functional testing, ergonomics evaluation, and stakeholder feedback, ultimately leading to a more optimized and successful final product design.
